同步回调
理解:立即执行,完全执行完了才结束,不会放入到回调队列中。
例子:数组遍历相关函数/Promise的执行函数
异步回调
理解:不会立即执行,会放到回调队列中将来执行
例子:定时器回调/ajax回调/Promisse的成功|失败的回调
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
const arr = [1,5,6];
arr.forEach(item => {
console.log(item);
})
console.log("同步函数回调");
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("setTimeout中的回调函数!!!");
},0)
console.log("异步函数回调!!");
|
为什么要用 Promise?
指定回调函数的方式更加灵活
- 旧的: 必须在启动异步任务前指定
- promise: 启动异步任务 => 返回promie对象 => 给promise对象绑定回调函 数(甚至可以在异步任务结束后指定/多个)
支持链式调用, 可以解决回调地狱问题
什么是回调地狱?
回调函数嵌套调用, 外部回调函数异步执行的结果是嵌套的回调执行的条件
回调地狱的缺点?
不便于阅读 不便于异常处理
解决方案?
promise 链式调用
Promise简单例子1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
function rand(m,n){
return Math.ceil(Math.random() * (n-m+1)) + m-1;
}
const btn = document.querySelector('#btn');
btn.addEventListener('click', function(){
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
let n = rand(1, 100);
if(n <= 30){
resolve(n);
}else{
reject(n);
}
}, 1000);
});
console.log(p);
p.then((value) => {
alert('恭喜恭喜, 奖品为 10万 RMB 劳斯莱斯优惠券, 您的中奖数字为 ' + value);
}, (reason) => {
alert('再接再厉, 您的号码为 ' + reason);
});
});
|
Promise简单例子2 (fs模块读取文件)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| const fs = require('fs');
let p = new Promise((resolve , reject) => {
fs.readFile('./resource/content.tx', (err, data) => {
if(err) reject(err);
resolve(data);
});
});
p.then(value=>{
console.log(value.toString());
}, reason=>{
console.log(reason);
});
|
Promise简单例子3 (fs模块读取文件)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
const btn = document.querySelector('#btn');
btn.addEventListener('click', function(){
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', 'https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke');
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300){
resolve(xhr.response);
}else{
reject(xhr.status);
}
}
}
});
p.then(value=>{
console.log(value);
}, reason=>{
console.warn(reason);
});
});
|
对Promise的简单封装(fs模块读取文件)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
function mineReadFile(path){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
require('fs').readFile(path, (err, data) =>{
if(err) reject(err);
resolve(data);
});
});
}
mineReadFile('./resource/content.txt')
.then(value=>{
console.log(value.toString());
}, reason=>{
console.log(reason);
});
|
对Promise的简单封装 AJAX 请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
function sendAJAX(url){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.responseType = 'json';
xhr.open("GET", url);
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300){
resolve(xhr.response);
}else{
reject(xhr.status);
}
}
}
});
}
sendAJAX('https://api.apiopen.top/getJok')
.then(value => {
console.log(value);
}, reason => {
console.warn(reason);
});
|
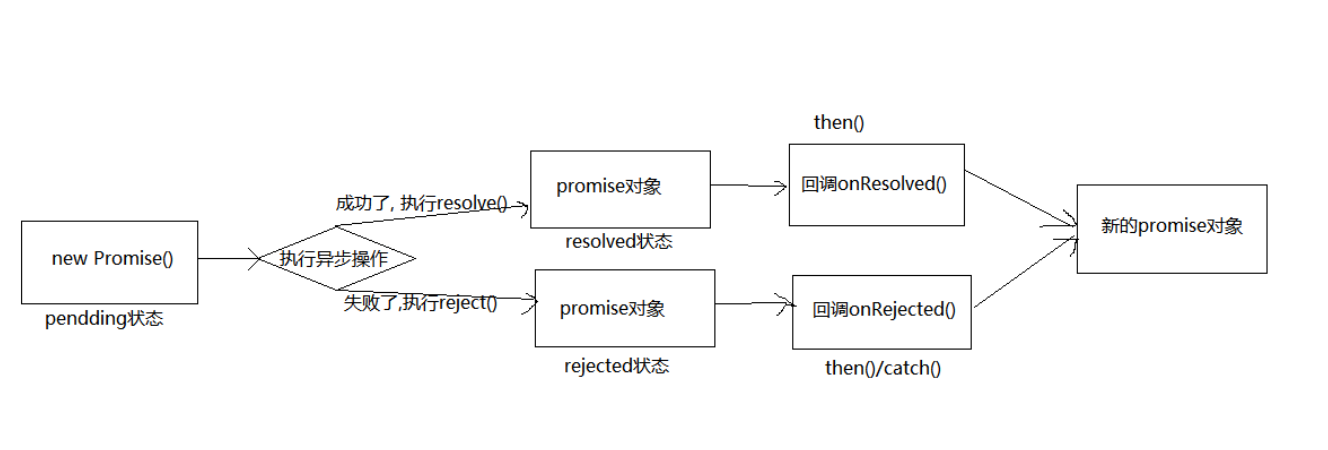
Pomise 的状态改变
pending 变为 resolved
pending 变为 rejected
说明: 只有这 2 种, 且一个 promise 对象只能改变一次
无论变为成功还是失败, 都会有一个结果数据
成功的结果数据一般称为 value, 失败的结果数据一般称为 reason
Promise 的基本流程
Promise API
Promise 构造函数: Promise (excutor) {}
(1) executor 函数: 执行器 (resolve, reject) => {}
(2) resolve 函数: 内部定义成功时我们调用的函数 value => {}
(3) reject 函数: 内部定义失败时我们调用的函数 reason => {} 说明: executor 会在 Promise 内部立即同步调用,异步操作在执行器中执行
Promise.prototype.then 方法: (onResolved, onRejected) => {}
(1) onResolved 函数: 成功的回调函数 (value) => {}
(2) onRejected 函数: 失败的回调函数 (reason) => {} 说明: 指定用于得到成功 value 的成功回调和用于得到失败 reason 的失败回调 返回一个新的 promise 对象
Promise.prototype.catch 方法: (onRejected) => {}
(1) onRejected 函数: 失败的回调函数 (reason) => {}
说明: then()的语法糖, 相当于: then(undefined, onRejected)
Promise.resolve 方法: (value) => {}
(1) value: 成功的数据或 promise 对象 说明: 返回一个成功/失败的 promise 对象
Promise.reject 方法: (reason) => {}
(1) reason: 失败的原因 说明: 返回一个失败的 promise 对象
Promise.all 方法: (promises) => {}
(1) promises: 包含 n 个 promise 的数组 说明: 返回一个新的 promise, 只有所有的 promise 都成功才成功, 只要有一个失败了就 直接失败
Promise.race 方法: (promises) => {}
(1) promises: 包含 n 个 promise 的数组 说明: 返回一个新的 promise, 第一个完成的 promise 的结果状态就是最终的结果状态
Promise 的几个关键问题
如何改变 promise 的状态?
(1) resolve(value): 如果当前是 pending 就会变为 resolved
(2) reject(reason): 如果当前是 pending 就会变为 rejected
(3) 抛出异常: 如果当前是 pending 就会变为 rejected
一个 promise 指定多个成功/失败回调函数, 都会调用吗?
当 promise 改变为对应状态时都会调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('OK');
});
p.then(value => {
console.log(value);
});
p
.then(value => {
alert(value);
});
|
改变 promise 状态和指定回调函数谁先谁后?
(1) 都有可能, 正常情况下是先指定回调再改变状态, 但也可以先改状态再指定回调
(2) 如何先改状态再指定回调?
① 在执行器中直接调用 resolve()/reject()
② 延迟更长时间才调用 then()
(3) 什么时候才能得到数据?
① 如果先指定的回调, 那当状态发生改变时, 回调函数就会调用, 得到数据
② 如果先改变的状态, 那当指定回调时, 回调函数就会调用, 得到数据
promise.then()返回的新 promise 的结果状态由什么决定?
(1) 简单表达: 由 then()指定的回调函数执行的结果决定
(2) 详细表达:
① 如果抛出异常, 新 promise 变为 rejected, reason 为抛出的异常
② 如果返回的是非 promise 的任意值, 新 promise 变为 resolved, value 为返回的值
③ 如果返回的是另一个新 promise, 此 promise 的结果就会成为新 promise 的结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('ok');
});
let result = p.then(value => {
}, reason => {
console.warn(reason);
});
console.log(result);
|
promise 如何串连多个操作任务?
(1) promise 的 then()返回一个新的 promise, 可以看成 then()的链式调用
(2) 通过 then 的链式调用串连多个同步/异步任务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('OK');
}, 1000);
});
p.then(value => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("success");
});
}).then(value => {
console.log(value);
}).then(value => {
console.log(value);
})
|
promise 异常传透?
(1) 当使用 promise 的 then 链式调用时, 可以在最后指定失败的回调,
(2) 前面任何操作出了异常, 都会传到最后失败的回调中处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('OK');
}, 1000);
});
p.then(value => {
throw '失败啦!';
}).then(value => {
console.log(222);
}).then(value => {
console.log(333);
}).catch(reason => {
console.warn(reason);
});
|
如何中断 Promise 链
(1) 当使用 promise 的 then 链式调用时, 在中间中断, 不再调用后面的回调函数
(2) 办法: 在回调函数中返回一个 pendding状态的 promise 对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('OK');
}, 1000);
});
p.then(value => {
console.log(111);
return new Promise(() => {});
}).then(value => {
console.log(222);
}).then(value => {
console.log(333);
}).catch(reason => {
console.warn(reason);
});
|
async和await
async 函数
- 函数的返回值为 promise 对象
- promise 对象的结果由 async 函数执行的返回值决定
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| async function main(){
throw "Oh NO";
}
let result = main();
console.log(result);
|
await 表达式
- await 右侧的表达式一般为 promise 对象, 但也可以是其它的值
- 如果表达式是 promise 对象, await 返回的是 promise 成功的值
- 如果表达式是其它值, 直接将此值作为 await 的返回值
- await 必须写在 async 函数中, 但 async 函数中可以没有 await
- 如果 await 的 promise 失败了, 就会抛出异常, 需要通过 try…catch 捕获处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| async function main(){
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject('Error');
})
try{
let res3 = await p;
}catch(e){
console.log(e);
}
}
main();
|
async与await的结合 案例1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
const fs = require('fs');
const util = require('util');
const mineReadFile = util.promisify(fs.readFile);
async function main(){
try{
let data1 = await mineReadFile('./resource/1.html');
let data2 = await mineReadFile('./resource/2.html');
let data3 = await mineReadFile('./resource/3.html');
console.log(data1 + data2 + data3);
}catch(e){
console.log(e.code);
}
}
main();
|
async与await的结合 案例2 (ajax )
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| function sendAJAX(url){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.responseType = 'json';
xhr.open("GET", url);
xhr.send();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300){
resolve(xhr.response);
}else{
reject(xhr.status);
}
}
}
});
}
let btn = document.querySelector('#btn');
btn.addEventListener('click',async function(){
let duanzi = await sendAJAX('https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke');
console.log(duanzi);
});
|



.jpg)
